
Contents
As we embrace renewable energy and shift towards more sustainable energy solutions, the limitations of traditional energy grids are more visible to us. These outdated systems and aging infrastructure are struggling to handle today’s unpredictable energy demands. Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar power and wind power, creates additional challenges for traditional grids due to their intermittent and variable nature. To meet the evolving energy landscape, we need smarter more flexible energy systems. AI in Smart Grid Management has been a game-changer for energy management. It is transforming energy systems by using real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance, and improving grid resilience. This allows energy systems to keep up with demand, predict issues, adapt to changes, and recover from disruptions. Let’s explore how AI is transforming energy grids and what the future holds.
What Makes a Grid “Smart”?
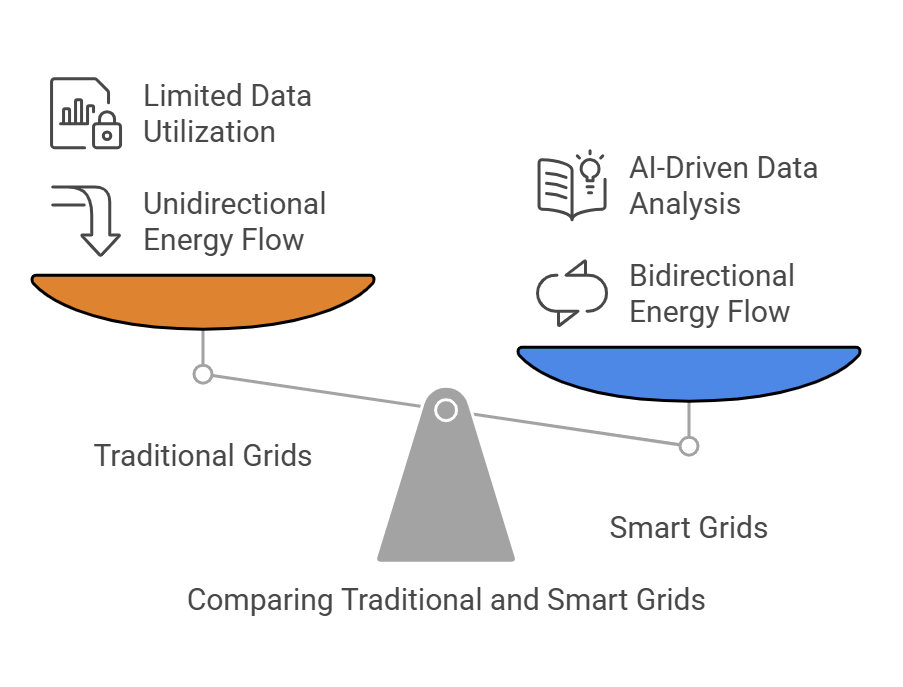
Traditional electrical grids, often referred to as ‘dumb’ grids have the energy flow in one direction. It flows from powerplants to homes and businesses. This outdated flow limits flexibility and efficiency. Smart grids, on the other hand, enable two-way energy flow, allowing power not only to flow from plants to consumers but also back into the grid from Distributed Energy Resources (DERs). DERs include renewable sources like solar panels and wind turbines. This capability makes the grid more decentralized, efficient, and sustainable.
Equipped with advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), smart grids leverage smart meters to collect and transmit real-time data on energy consumption to utilities and consumers. It optimizes energy usage, identifies inefficiencies, and helps users make informed decisions about energy consumption and production. This enhanced visibility and control ultimately lead to improved energy efficiency and grid stability.
However, the real magic takes place when smart grid technology is integrated with AI. AI analyzes massive data generated by smart meters and other grid components and recognizes patterns, detects anomalies, and predicts trends. AI, makes grids smarter, more reliable, and gives it the ability to meet the evolving energy needs of the future.1
Find Your Perfect Software Outsourcing Partner
Unlock a world of trusted software outsourcing companies and elevate your business operations seamlessly.
Discover CompaniesThe Role of AI in Smart Grid Management
AI is making smart grid management better by processing massive amounts of data in real time in the background. Acting as the brain of the grid, it rapidly interprets sensor signals, predicts future scenarios, and determines the best course of action, often in milliseconds.
This capability allows for proactive management of the grid, rather than simply reacting to events as they occur. By analyzing patterns and trends in the data, AI can predict potential faults or outages before they happen, enabling preventative measures to be taken. This not only improves the reliability and stability of the grid but also reduces costs associated with unplanned downtime and repairs.
Furthermore, AI’s ability to optimize grid operations in real-time leads to increased efficiency and resource utilization. For instance, AI can balance supply and demand by intelligently managing the distribution of electricity, ensuring that power is directed where it’s needed most. This can also facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, which can be unpredictable and intermittent, into the grid.
Challenges in AI-powered Future
While the integration of AI into the energy sector holds promise for a smarter and more efficient grid, it also presents a new set of challenges that must be addressed. The reliance on interconnected digital technologies and the vast amount of data flowing through these systems create vulnerabilities that could be exploited. Cyberattacks targeting smart grids could disrupt power distribution, cause blackouts, and potentially damage critical infrastructure.
Therefore, building strong cybersecurity is essential. This includes implementing advanced systems, protocols, and audits to identify and address security vulnerabilities. Energy companies must train staff to handle cyber threats. Collaboration between government agencies, energy providers, and technology companies is also essential to share information and develop best practices for securing smart grids. Ensuring the reliability of AI systems is vital as they become more integrated into grid management. AI algorithms need to be transparent and explainable to ensure that their decision-making processes can be understood and trusted. Additionally, AI systems need protection from manipulation or bias to prevent compromised grid stability.
Future of AI and Smart Grids
The evolution of energy management is trending towards decentralization. Artificial intelligence plays a pivotal role in this shift, enabling localized energy systems like microgrids to function autonomously. This is especially useful in remote areas or disaster zones where the main grid is not accessible. AI-driven microgrids can manage power generation, storage, and distribution, ensuring reliable and resilient power supply even when disconnected from the main grid.
AI and other emerging technologies will significantly change the energy sector. Blockchain, for instance, offers a transparent and secure way to track and trade energy between consumers and providers. This could enable peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals to sell surplus renewable energy directly to others, creating a more dynamic and democratized energy market. Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate these transactions, ensuring trust and efficiency without intermediaries.
In essence, the convergence of AI, smart grid technologies, and innovations like blockchain is paving the way for a future where energy is not only smarter and more efficient but also more decentralized and accessible. This transformation has the potential to enhance grid resilience, reduce carbon emissions, and empower consumers to take a more active role in managing their energy consumption.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence has transitioned smart grids beyond mere upgrades, transforming them into responsive, adaptive systems that can meet the challenges of modern energy demands. By predicting needs, optimizing operations, and integrating renewable energy sources, AI increases the efficiency, sustainability, and resilience of power grids. As energy providers face increasingly complex challenges, AI has become a crucial tool for improving energy consumption and creating a more dependable and sustainable energy future.






