
Contents
Over the past 30 years, companies have focused on automating and maintaining back-end systems. As these systems grew more complex, businesses allocated a large share of their IT budgets to operations. Technology now influences every aspect of business, driving significant investment. According to Deloitte’s 2023 study, the average tech budget is 5.49% of revenue, up from 4.25% in 2020.1 Companies see technology as a key factor in their success or failure. Companies recognize that strategic IT investment plays a pivotal role in their success or failure.
Industry Trends in Technology Spending
Deloitte’s 2018 Global CIO Survey found that technology spending varies by industry. Banking and securities allocate over 7.9% of revenue to technology, while construction and infrastructure spend less than 2%. Some industries, like healthcare, insurance, and travel, are increasing IT budgets to modernize outdated systems and integrate new digital technologies. This improves customer engagement and enhances digital capabilities. Companies can use increased budgets to drive growth, By aligning IT spending with business strategy.
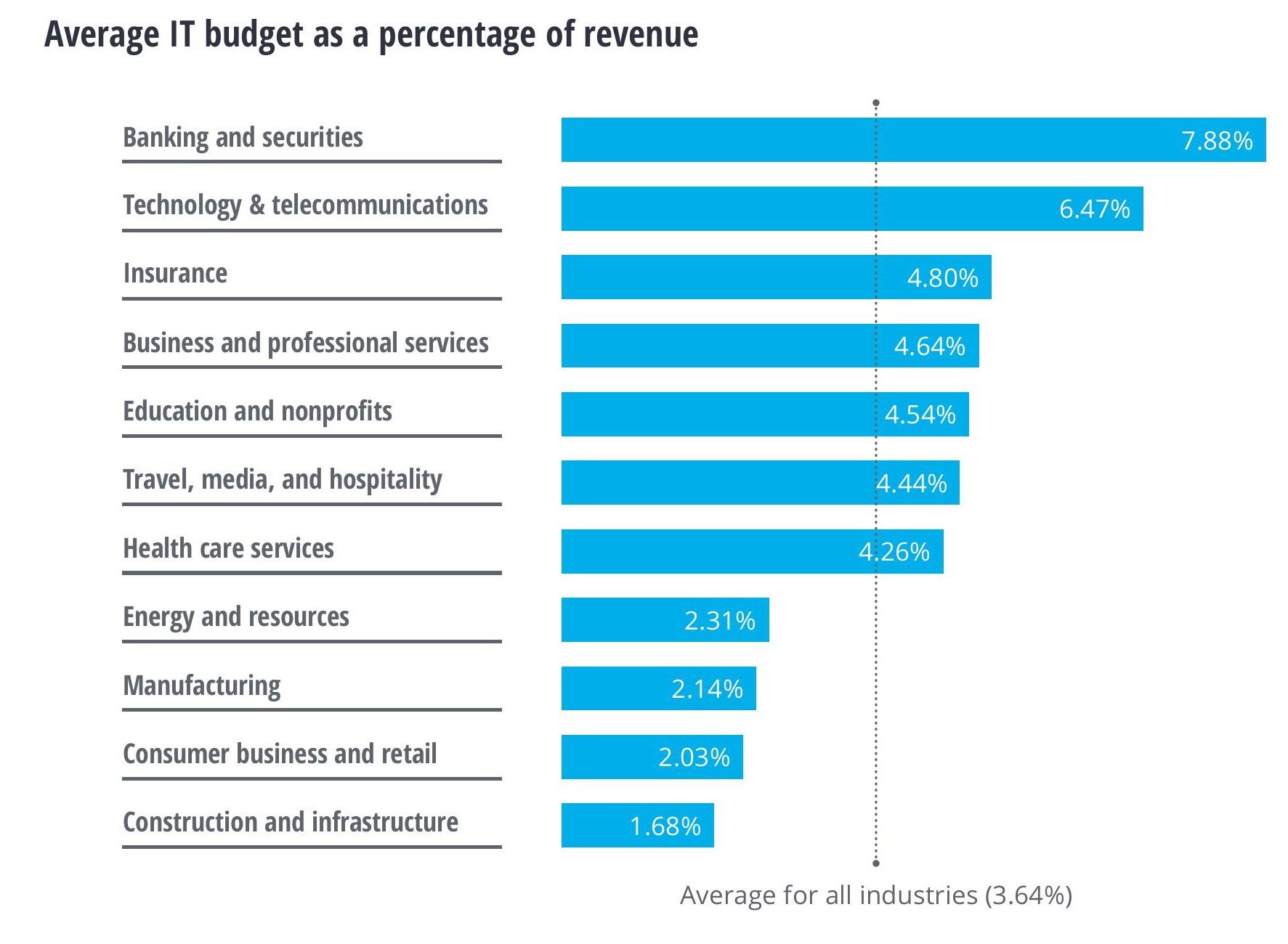
IT Spending Budget Allocations
To optimize IT budgets and align them with business strategy, companies must reassess spending across all IT categories. Embracing Agile, and DevOps practices while adopting cloud technology is now essential. This shift requires changes in IT operations and cost structures to track investments in business operations, incremental changes, and innovation. Since the Global CIO Survey is our main source, we have discussed IT spending categories focusing on the role of Chief Information Officers.
Business Operations
Cloud migration has significantly reduced operational costs over the past decade. Streamlining business operations frees up budget for initiatives that drive change and innovation, enabling CIOs to impact revenue growth. For example, a consumer goods company CIO cut over $150 million in IT costs over three years, according to Deloitte. His cost-saving efforts enhanced his credibility and allowed him to reinvest half the savings into innovation.
Incremental Business Change
CIOs leading large-scale tech projects like ERP or CRM overhauls focus on execution to drive change and revenue growth. In these cases, delivering business value outweighs cost reduction. However, managing complex transformations can be challenging. Unnecessary customizations and delays often lead to cost overruns. For example, a new CIO at a major retailer discovered his team was handling over 200 projects, many without a clear business owner. He froze all projects and required each to have a sponsor, terminating those without one.
Business Innovation
Innovation investments allow CIOs to drive revenue growth, but understanding their long-term costs is crucial, as today’s innovation can become tomorrow’s operational expense. To optimize returns, many CIOs are leveraging external resources, partnering with innovation labs, tech hubs, incubators, accelerators, venture capital, and private equity firms for rapid innovation.
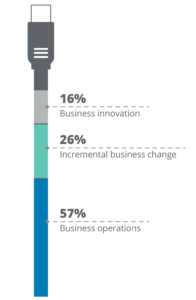 |
The majority of CIOs’ technology budgets (57%) are allocated to supporting business operations. Comparatively, 26% of the budget is allocated to funding incremental business change and 16% to innovation. |
IT budget allocation is influenced by factors such as industry, market conditions, and business strategy. Risk appetite and priorities also play a key role in technology investment decisions. For example, a government agency may delay adopting costly, unproven technologies, while a retail bank may pursue innovation to stay competitive. Companies with higher risk tolerance might invest in emerging technologies with high potential returns but greater uncertainty. On the other hand, risk-averse companies tend to favor established technologies. A company focused on innovation may invest more in R&D and emerging technologies, whereas one focused on cost reduction may prioritize efficiency. According to the latest CIO survey, organizations labeled as digital vanguards have four spending habits that set them apart from baseline organizations.2
-
- They spend more on innovation.
- They spend twice as much on technology.
- They practice better technology governance.
- They use metrics more effectively.
Strategic IT investment and budget allocation decisions depend largely on an organization’s type and external environment. Companies in rapidly evolving industries, like technology, require substantial investment to stay competitive. One the other hand, companies in stable industries, like utilities, may invest less in new technologies. For example, technology, telecommunications, insurance, and banking firms are increasing spending on innovation to build new capabilities and enhance customer engagement. Meanwhile, traditionally slower adopters like healthcare and energy are now investing more in innovation as their industries undergo digital transformation.
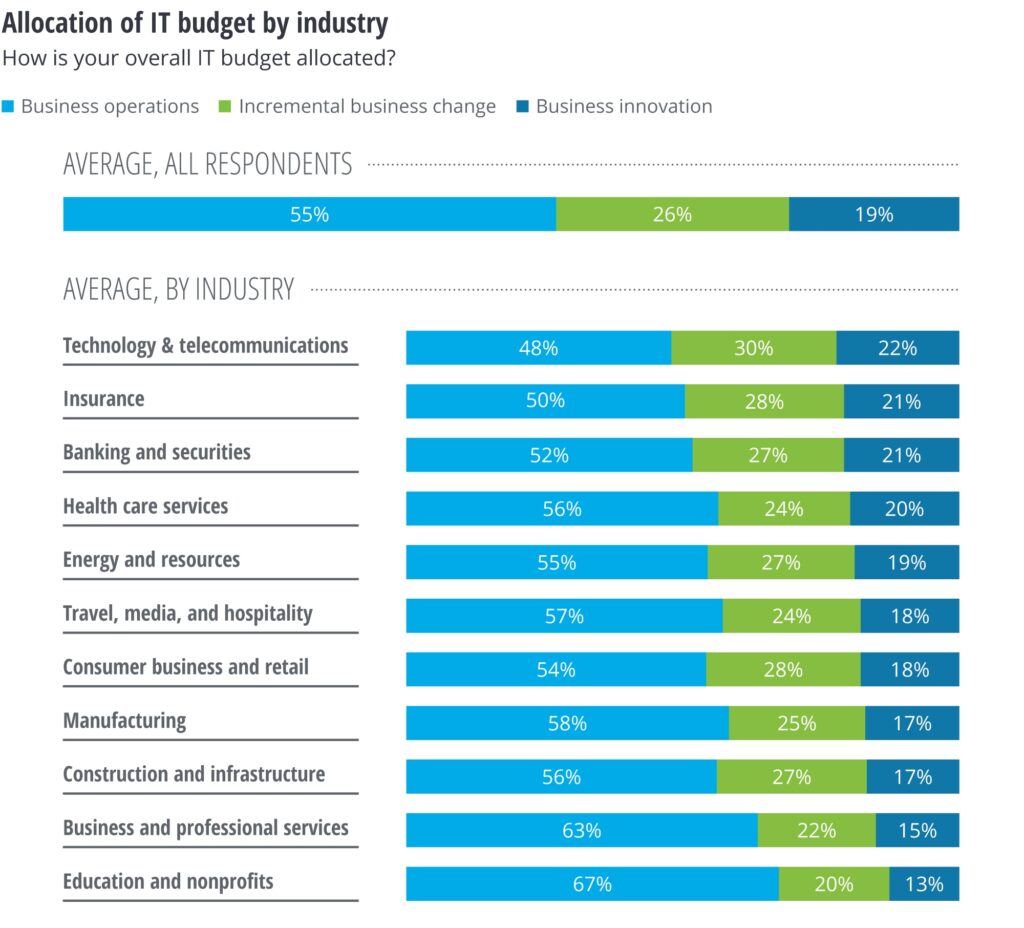
Changing Perspective: Viewing Technology as an Investment, Not an Expense
As technology and business strategies merge, IT is shifting its focus from service delivery to value delivery. While maintaining operations is critical, technology teams must also collaborate with business functions to create value. However, many CIOs report a disconnect between business leadership’s expectations and IT budget allocation.3 While 72% of CIOs say executives prioritize revenue-generating and innovative projects4, 55% of IT budgets still go toward maintaining operations, with only 19% spent on innovation.5
IT has long been seen as a cost center, posing a challenge for CIOs. By integrating technology with business strategy, CIOs can shift from cost-cutting to strategic IT investments that drive revenue, growth, and financial performance.
Find Your Perfect Software Outsourcing Partner
Unlock a world of trusted software outsourcing companies and elevate your business operations seamlessly.
Discover CompaniesKey Recommendations for Investing in IT
- Know the business strategy: Co-creating value requires integrating business and technology strategies. A unified strategy defines technology’s role in driving business value and guides investment decisions.
- Focus on company financials: Organizations track key financial indicators like market share, ROI, earnings per share, and profitability. Understanding how technology impacts these KPIs is crucial, with ROI being the most critical measure for justifying investments.
- Build a balanced portfolio: CIOs are diversifying tech investments by allocating funds based on time horizons, risk, reward, and value. They balance tech investments between current business operations, improving capabilities, and new opportunities, depending on the corporate strategy and market conditions.
- Employ risk management tools: Risk adversity varies with leadership, competition, and market shifts. Management should establish governance frameworks that reflect shared risk tolerance, using parameters like ROI, acceptable return rates, and long-term investment horizons.
- Expect volatility: To keep up with rapid technological changes, companies require flexible investment strategies. Fixed budgets and rigid annual cycles can hinder agility. Regular reevaluation helps ensure investments remain aligned with business needs.
- Keep operational expenses low: Effectively managing IT expenses builds credibility and opens the door for greater investment. For example, a CIO at a consumer goods company reduced IT costs by 25% over two years, earning leadership’s trust and ultimately securing a sixfold increase in technology investments.
Conclusion
Technology spending is now a key driver of business growth. Companies are aligning IT budgets with strategy to boost revenue, innovation, and efficiency. While resource allocation varies by industry, digitally advanced leaders prioritize innovation. To maximize strategic IT investment, CIOs must balance operations, manage risks, and adapt to change. As technology shifts from a cost center to a strategic asset, it is becoming vital to business success.
References
[1] From tech investment to impact: Strategies for allocating capital and articulating value ↩
[2] Reinventing tech finance: The evolution from IT budgets to technology investments ↩
[3] How CIOs can industrialize business innovation ↩






