Contents
Whether you grew up with technology or just pride yourself on being extra cautious online, chances are your cyber safety has been at risk without you even realizing it. Here’s a shocking fact: in 2024 alone, Australians have already lost over $186 million to online scams1.
In today’s digital world, maintaining cybersecurity best practices is not just important- it is non-negotiable. With cyber threats growing daily, businesses need strong security measures. We have all seen the headlines about companies paying massive fines or, worse, shutting down because of a single cyber-attack. From ransomware to phishing scams, the risks are everywhere, and ignoring them could cost you your savings, your identity, or even your entire business.
The key? Prevention. Here are 5 essential cybersecurity best practices that can help safeguard your organization.
What is a Cyberattack?
A cyberattack is an attempt by hackers or malicious actors to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, or data. These attacks can come in various forms, such as malware, ransomware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks, and they aim to steal sensitive information, corrupt data, or halt operations.
Cyberattacks have a significant impact on a company’s operations, financial performance, and safeguarding of sensitive information. Let’s understand what happened to this automotive company.
Kawasaki Motors Europe recently faced a major cyberattack that forced them to take their servers offline to contain the damage. The attackers managed to steal 487GB of critical data, including financial details, banking records, dealership info, and internal communications. Later that month, Kawasaki Motors Europe successfully recovered most of its servers and resumed business with third-party suppliers and dealers. To prevent future breaches, they enhanced their monitoring operations and tightened access restrictions. This incident serves as a stark reminder of the importance of robust cybersecurity measures2.
Types of Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks are not always about stealing money. Some are designed to damage systems or gain access to sensitive information. Both individuals and organizations must be aware of the different types of cyber threats they may face.
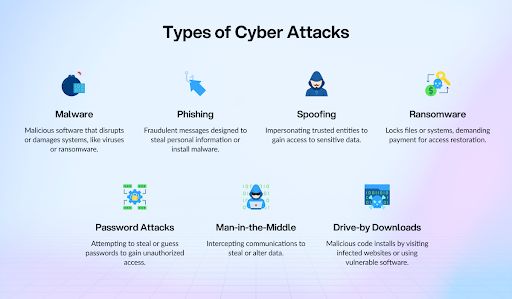
- Malware
Malware (short for Malicious Software) refers to harmful software like viruses, ransomware, spyware, and worms that attackers use to infiltrate systems. Clicking on a suspicious link or attachment can activate malware, allowing it to steal data or disrupt operations.
- Phishing
Phishing scams often come through emails or messages that look legitimate but are actually designed to trick you into sharing personal details, such as credit card numbers. These scams may also install malware on your device if you follow their instructions.
- Spoofing
In spoofing attacks, cybercriminals disguise themselves as trusted individuals or organizations to deceive victims into revealing sensitive data. They may use fake caller IDs, counterfeit websites, or even manipulate facial recognition systems to gain access.
- Ransomware
Ransomware locks users out of their devices or files until a ransom is paid. However, paying does not always ensure access is restored, which is why experts often recommend against giving in to the demands of attackers.
- Password Attacks
These attacks involve hackers attempting to guess or steal passwords through various methods. They may use keylogging (tracking what you type), phishing scams, or simply guessing common passwords to break into accounts.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Attacks
IoT devices- such as smart home gadgets, cameras, or wearables, are often connected to the internet with minimal security. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in these networks to access sensitive data or control devices remotely.
- Drive-by Downloads
Drive-by downloads happen when malicious code is installed on a device simply by visiting an infected website or using vulnerable software. Unlike other attacks, no user action is required, just landing on the wrong site can be enough.
With the rise of threats like malware and drive-by-downloads, no organization is safe, making robust cybersecurity measures essential in today’s digital landscape.
5 Cybersecurity Best Practices to Prevent Cyberattacks
The first step in preventing cyberattacks is awareness. Ensuring that you and other employees at the organization understand the risks can make a significant difference. Simple habits, like verifying email addresses and thinking twice before clicking on links, help safeguard sensitive data and systems.

- Use a Firewall
Firewalls act as a protective barrier, filtering network traffic and blocking unauthorized access. They help prevent attacks like backdoor intrusions and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks by stopping harmful activity before it reaches your system, making it a cybersecurity best practice essential.
- Encrypt Your Data
Encryption keeps data secure by making it unreadable to anyone without the correct decryption key. This extra layer of protection makes it extremely difficult for attackers to access sensitive information, even if they manage to breach your system.
- Keep Your Software Updated
Regularly updating your software strengthens security by fixing vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit. Older versions often have known weaknesses, so staying up to date is crucial. Consider using a patch management system to automate updates and keep all software secure.
- Use Strong & Unique Passwords
Weak or reused passwords make it easier for hackers to gain access. Strengthen your security by using complex passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Change them regularly and avoid using the same password across multiple accounts.
- Back-Up Your Data
Regularly backing up important files ensures that you can recover lost data if an attack occurs and falls under cybersecurity best practices. Store backups securely, whether in the cloud or on an external drive, so you always have access to critical information.
Find Your Perfect Software Outsourcing Partner
Unlock a world of trusted software outsourcing companies and elevate your business operations seamlessly.
Discover CompaniesHow to Bounce Back After a Cyberattack
If you fall victim to a cyberattack, take immediate action to minimize the damage:
- Report to Authorities – File a First Information Report (FIR) at your nearest police station or report the incident to your country’s cybercrime reporting portal. Quick reporting can help law enforcement track and mitigate cyber threats.
- Notify Relevant Organizations – If your bank account, credit card, or financial details have been compromised, contact your bank immediately to freeze or block unauthorized transactions. Also, inform other service providers, such as email or telecom operators, if your accounts are at risk.
- Disconnect from the Internet – If the device is infected with malware or ransomware, disconnect from the Internet to prevent further access by attackers.
- Change Passwords and Enable Security Measures – Update all compromised passwords immediately. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible for extra security.
- Run a Security Scan – Use antivirus software to scan your device and remove any malware. If necessary, seek help from cybersecurity professionals to restore your system safely.
- Inform Affected Parties – If sensitive business or customer data has been exposed, notify all affected individuals and follow any legal or regulatory requirements for data breaches.
To Conclude
To effectively combat the relentless wave of cyberattacks, cybersecurity best practices and budgets must be adaptable to evolving threats and capable of deploying new security measures as needed. Using AI to support security teams is now extremely crucial, and business owners can enhance their company’s safety and cybersecurity by outsourcing services from countries like India, Bangladesh, and Ukraine, where skilled professionals can provide robust security solutions at a more affordable rate.
References
[1] Scam statistics ↩
[2] Kawasaki Motors Europe (KME) faces 487GB data leak after cyberattack ↩